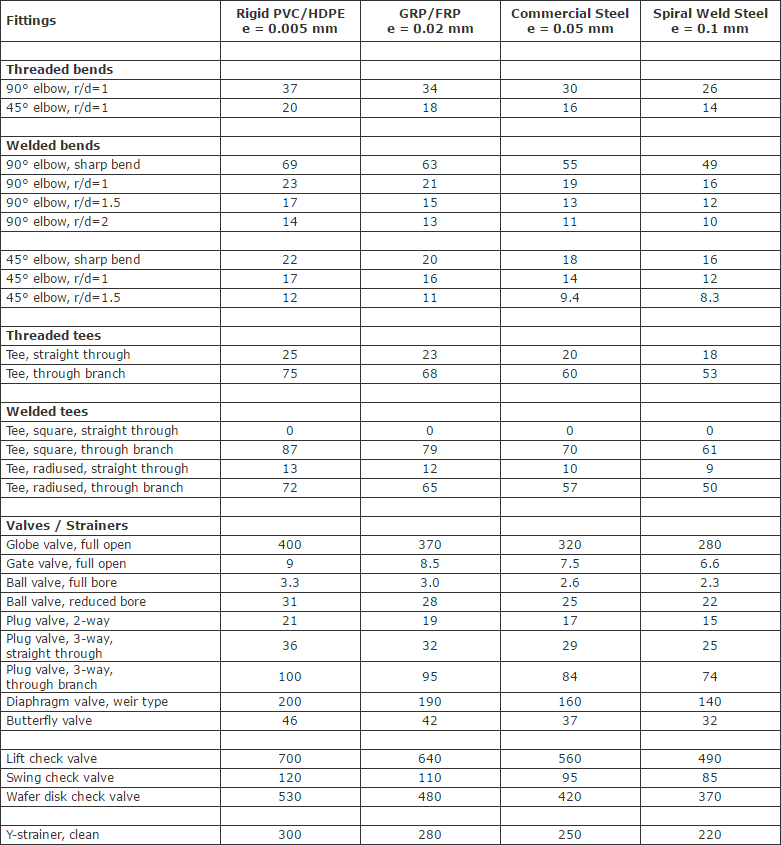
K Value Fittings . H = pressure loss in terms of fluid head, i.e. the 3k method allows the user to characterise the pressure loss for flow through fittings in a pipe. the three common methods for calculating the head loss in valves and fittings are: The l/d coefficient (pronounced l over d) the. Determine l (friction loss in pipe fittings in terms of equivalent length in feet of straight pipe). H = k x v² / 2g. 32 rows the pressure drop through common fittings and valves found in fluid piping can be calculated thanks to a friction coefficient k. fluid head loss through a fitting can be calculated by the following equation:
from divi.aft.com
The l/d coefficient (pronounced l over d) the. fluid head loss through a fitting can be calculated by the following equation: the three common methods for calculating the head loss in valves and fittings are: the 3k method allows the user to characterise the pressure loss for flow through fittings in a pipe. H = k x v² / 2g. H = pressure loss in terms of fluid head, i.e. Determine l (friction loss in pipe fittings in terms of equivalent length in feet of straight pipe). 32 rows the pressure drop through common fittings and valves found in fluid piping can be calculated thanks to a friction coefficient k.
Using Equivalent Lengths in AFT Fathom AFT Wordpress Dev
K Value Fittings the three common methods for calculating the head loss in valves and fittings are: Determine l (friction loss in pipe fittings in terms of equivalent length in feet of straight pipe). The l/d coefficient (pronounced l over d) the. the 3k method allows the user to characterise the pressure loss for flow through fittings in a pipe. the three common methods for calculating the head loss in valves and fittings are: H = k x v² / 2g. 32 rows the pressure drop through common fittings and valves found in fluid piping can be calculated thanks to a friction coefficient k. H = pressure loss in terms of fluid head, i.e. fluid head loss through a fitting can be calculated by the following equation:
From www.corzan.com
How Fittings, Valves and Strainers Affect Pressure Drop and Head Loss Corzan K Value Fittings H = pressure loss in terms of fluid head, i.e. the 3k method allows the user to characterise the pressure loss for flow through fittings in a pipe. Determine l (friction loss in pipe fittings in terms of equivalent length in feet of straight pipe). fluid head loss through a fitting can be calculated by the following equation:. K Value Fittings.
From www.researchgate.net
The slope K value of fitting curve Download Scientific Diagram K Value Fittings The l/d coefficient (pronounced l over d) the. H = k x v² / 2g. fluid head loss through a fitting can be calculated by the following equation: 32 rows the pressure drop through common fittings and valves found in fluid piping can be calculated thanks to a friction coefficient k. the three common methods for calculating. K Value Fittings.
From katmarsoftware.com
Resistance coefficients (K values) for pipe fittings like bends, tees, valves and orifices K Value Fittings the three common methods for calculating the head loss in valves and fittings are: Determine l (friction loss in pipe fittings in terms of equivalent length in feet of straight pipe). The l/d coefficient (pronounced l over d) the. H = k x v² / 2g. fluid head loss through a fitting can be calculated by the following. K Value Fittings.
From www.academia.edu
(PDF) Friction Losses in Pipe Fittings Resistance Coefficient K (use in formula hf = Kv²/2g K Value Fittings the 3k method allows the user to characterise the pressure loss for flow through fittings in a pipe. H = pressure loss in terms of fluid head, i.e. the three common methods for calculating the head loss in valves and fittings are: The l/d coefficient (pronounced l over d) the. H = k x v² / 2g. Determine. K Value Fittings.
From web.deu.edu.tr
Toprak Home Page K Value Fittings the three common methods for calculating the head loss in valves and fittings are: the 3k method allows the user to characterise the pressure loss for flow through fittings in a pipe. The l/d coefficient (pronounced l over d) the. fluid head loss through a fitting can be calculated by the following equation: Determine l (friction loss. K Value Fittings.
From www.jainsonsindustries.com
Manufacturer & Exporter of Grooved fittings for Plumbing, Fire Fighting & Gas Distribution K Value Fittings fluid head loss through a fitting can be calculated by the following equation: H = k x v² / 2g. 32 rows the pressure drop through common fittings and valves found in fluid piping can be calculated thanks to a friction coefficient k. Determine l (friction loss in pipe fittings in terms of equivalent length in feet of. K Value Fittings.
From www.scribd.com
Ductile Iron Fittings Weight Chart Gas Technologies Building Materials K Value Fittings H = pressure loss in terms of fluid head, i.e. Determine l (friction loss in pipe fittings in terms of equivalent length in feet of straight pipe). 32 rows the pressure drop through common fittings and valves found in fluid piping can be calculated thanks to a friction coefficient k. the three common methods for calculating the head. K Value Fittings.
From engineeringness.com
Pressure Drop In Pipe Lines And Fittings Part 2 Engineeringness K Value Fittings fluid head loss through a fitting can be calculated by the following equation: the three common methods for calculating the head loss in valves and fittings are: the 3k method allows the user to characterise the pressure loss for flow through fittings in a pipe. The l/d coefficient (pronounced l over d) the. H = pressure loss. K Value Fittings.
From katmarsoftware.com
Resistance coefficients (K values) for pipe fittings like bends, tees, valves and orifices K Value Fittings Determine l (friction loss in pipe fittings in terms of equivalent length in feet of straight pipe). H = pressure loss in terms of fluid head, i.e. The l/d coefficient (pronounced l over d) the. H = k x v² / 2g. fluid head loss through a fitting can be calculated by the following equation: the three common. K Value Fittings.
From bisonoilfield.com
BISON Fitting K Value Fittings fluid head loss through a fitting can be calculated by the following equation: 32 rows the pressure drop through common fittings and valves found in fluid piping can be calculated thanks to a friction coefficient k. H = k x v² / 2g. Determine l (friction loss in pipe fittings in terms of equivalent length in feet of. K Value Fittings.
From www.pumpsandsystems.com
Understand How Valves & Fittings Affect Head Loss Pumps & Systems K Value Fittings The l/d coefficient (pronounced l over d) the. the three common methods for calculating the head loss in valves and fittings are: Determine l (friction loss in pipe fittings in terms of equivalent length in feet of straight pipe). the 3k method allows the user to characterise the pressure loss for flow through fittings in a pipe. H. K Value Fittings.
From divi.aft.com
Using Equivalent Lengths in AFT Fathom AFT Wordpress Dev K Value Fittings H = k x v² / 2g. H = pressure loss in terms of fluid head, i.e. The l/d coefficient (pronounced l over d) the. 32 rows the pressure drop through common fittings and valves found in fluid piping can be calculated thanks to a friction coefficient k. Determine l (friction loss in pipe fittings in terms of equivalent. K Value Fittings.
From www.thermal-engineering.org
What is Resistance Coefficient Method K Method Excess head Definition K Value Fittings the 3k method allows the user to characterise the pressure loss for flow through fittings in a pipe. Determine l (friction loss in pipe fittings in terms of equivalent length in feet of straight pipe). the three common methods for calculating the head loss in valves and fittings are: fluid head loss through a fitting can be. K Value Fittings.
From energy-models.com
Piping Design Program K Value Fittings Determine l (friction loss in pipe fittings in terms of equivalent length in feet of straight pipe). H = pressure loss in terms of fluid head, i.e. H = k x v² / 2g. the 3k method allows the user to characterise the pressure loss for flow through fittings in a pipe. fluid head loss through a fitting. K Value Fittings.
From www.researchgate.net
Typical local loss coefficient k. Download Scientific Diagram K Value Fittings 32 rows the pressure drop through common fittings and valves found in fluid piping can be calculated thanks to a friction coefficient k. H = k x v² / 2g. H = pressure loss in terms of fluid head, i.e. the 3k method allows the user to characterise the pressure loss for flow through fittings in a pipe.. K Value Fittings.
From www.youtube.com
MCET212 K factor for pipe fittings calculation part YouTube K Value Fittings The l/d coefficient (pronounced l over d) the. fluid head loss through a fitting can be calculated by the following equation: H = pressure loss in terms of fluid head, i.e. Determine l (friction loss in pipe fittings in terms of equivalent length in feet of straight pipe). H = k x v² / 2g. the 3k method. K Value Fittings.
From www.hvacbrain.com
What is the K factor and how do we use it in HVAC applications? Hvac Brain Northrich Parts K Value Fittings The l/d coefficient (pronounced l over d) the. fluid head loss through a fitting can be calculated by the following equation: the three common methods for calculating the head loss in valves and fittings are: Determine l (friction loss in pipe fittings in terms of equivalent length in feet of straight pipe). H = pressure loss in terms. K Value Fittings.
From www.researchgate.net
The bestfitting average k values com puted for kNN and kNCN and the... Download Table K Value Fittings The l/d coefficient (pronounced l over d) the. the three common methods for calculating the head loss in valves and fittings are: Determine l (friction loss in pipe fittings in terms of equivalent length in feet of straight pipe). H = k x v² / 2g. 32 rows the pressure drop through common fittings and valves found in. K Value Fittings.